[TopCoder12727]FoxAndCity 题解
题目地址:TopCoder Arena:Practice – TopCoder …
May all the beauty be blessed.
题目地址:TopCoder Arena:Practice – TopCoder Arena、vjudge:CurvyonRails – TopCoder 12432 – Virtual Judge
Cat Carol is the queen of Gridland. Gridland is a rectangular country divided into a grid of unit square cells. Each cell contains either a town or a wasteland. Carol has decided to construct some railroad tracks according to the following rules:
Note that Carol does not require the entire set of tracks to be connected. Configurations that consist of multiple disjoint loops are acceptable, too.
A Curvy is a curious animal indigenous to Gridland. These animals love curves and hate straight things. Some of the towns in Gridland are inhabited by Curvies. If such a town happens to contain a straight segment of tracks (i.e., a segment that connects two opposite sides of the cell), the Curvies in the town are very unhappy.
You are given a String[] field that describes Gridland: each character of each element of field describes one of its cells. The meaning of individual characters follows.
Compute and return the minimal number of towns with unhappy Curvies when the railroad tracks are constructed according to the above constraints. If there is no way to construct the railroads according to the given rules, return -1 instead.
要求在一个方格图上修建火车轨道,使得轨道都能构成自环。注意有一些格子有障碍,还有些格子在放置直轨道的时候产生费用。
类名:CurvyonRails
函数名:getmin
参数:vector <string>
返回值:int
函数声明:int getmin(vector <string> field)
样例#1:
.. ..
样例#1结果:
0
其他样例参见原网站。
参考资料:Topcoder SRM570 900 CurvyonRails – Enigma_aw – 博客园
如果把方格图抽象成普通图,一条轨道会使一个格子产生2的度数。我们考虑对这个方格图黑白染色,以便控制度数/流量平衡的条件,即度数为2。在这里不使用拆点的方法是因为图是无向图,不需要区分出度与入度。
我们可以建立一个源→黑点→白点→汇的网络,其中,所有的边都设置成容量2的边,用于限制度数。但是这样的图显然是不能够符合要求的,因为我们还要区分直轨弯轨与费用问题。对于直轨弯轨,我们发现直轨只产生横向或纵向的2个度数,而弯轨产生的度数是横纵各1的。我们对一个点拆成横向度数和纵向度数两个点,在黑白点的连接时也区分横纵度数连边即可。我们再用一个总点来限流,即现在的网络变为了源→黑点→黑点的横/纵点→白点的横/纵点→白点→汇,其中源→黑点→黑点的横/纵点之间的边都为容量2的边(白点类似)。至于费用问题,由于我们已经区分了横纵点,对于直轨会产生费用的点,我们从总点向横/纵点建边时建一条容量1费用0的边,再建一条容量1费用1的边,就可以表示如果同一方向产生2个度数产生的费用了。
网络上跑最小费用最大流即可,如果不能满流,说明无解。
由于TopCoder要求实现一个class,下面的代码并不是标准输入/输出格式(传统OI题目)的实现方式,但是把调试注释给去掉就可以用标准输入/输出了。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, cap, cost, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 1];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void reset() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); tot = 0;
}
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int cap, int cost) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, cap, cost, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, 0, -cost, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int dis[MAXN], f[MAXN], pre[MAXN], pree[MAXN];
std::queue<int> que;
bool inque[MAXN];
inline bool spfa(int s, int t) {
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
que.push(s); inque[s] = true; f[s] = INF; dis[s] = 0;
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop(); inque[u] = false;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && dis[v] > dis[u] + gra[i].cost) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + gra[i].cost;
f[v] = std::min(f[u], gra[i].cap);
pre[v] = u; pree[v] = i;
if(!inque[v]) {
inque[v] = true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return f[t] > 0;
}
int flow, cost;
inline void mcmf(int s, int t) {
while(spfa(s, t)) {
flow += f[t];
cost += f[t] * dis[t];
for(int i = t; i != s; i = pre[i]) {
gra[pree[i]].cap -= f[t]; gra[pree[i] ^ 1].cap += f[t];
}
}
}
int n, m, S, T;
class CurvyonRails {
public:
inline int getmin(std::vector<std::string> field) {
n = field.size(); m = field[0].size();
S = n * m * 3 + 1; T = S + 1;
reset();
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int ii = i - 1, jj = j - 1;
if(field[ii][jj] == 'w') continue;
if(!((i + j) & 1)) {
sum += 2;
addedge(S, (i - 1) * m + j, 2, 0);
if(field[ii][jj] != 'C') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m, 2, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, 2, 0);
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m, 1, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, 1, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m, 1, 1);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, 1, 1);
}
if(j - 1 >= 1 && field[ii][jj - 1] != 'w') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m, (i - 1) * m + j - 1 + n * m, 1, 0);
}
if(j + 1 <= m && field[ii][jj + 1] != 'w') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m, (i - 1) * m + j + 1 + n * m, 1, 0);
}
if(i - 1 >= 1 && field[ii - 1][jj] != 'w') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2,
(i - 2) * m + j + n * m * 2, 1, 0);
}
if(i + 1 <= n && field[ii + 1][jj] != 'w') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, i * m + j + n * m * 2, 1, 0);
}
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, T, 2, 0);
if(field[ii][jj] != 'C') {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m, (i - 1) * m + j, 2, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, (i - 1) * m + j, 2, 0);
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m, (i - 1) * m + j, 1, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, (i - 1) * m + j, 1, 0);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m, (i - 1) * m + j, 1, 1);
addedge((i - 1) * m + j + n * m * 2, (i - 1) * m + j, 1, 1);
}
}
}
}
mcmf(S, T);
if(flow < sum) {
return -1;
} else {
return cost;
}
}
};
/*int main() {
std::string t;
std::vector<std::string> field;
while(!getline(std::cin, t).eof()) {
field.push_back(t);
}
CurvyonRails solver;
printf("%d", solver.getmin(field));
return 0;
}*/
题目地址:洛谷:【P4307】[JSOI2009]球队收益 / 球队预算 – 洛谷、BZOJ:Problem 1449. — [JSOI2009]球队收益
在一个篮球联赛里,有n支球队,球队的支出是和他们的胜负场次有关系的,具体来说,第i支球队的赛季总支出是Cix^2+Diy^2,Di<=Ci。(赢得多,给球员的奖金就多嘛) 其中x,y分别表示这只球队本赛季的胜负场次。现在赛季进行到了一半,每只球队分别取得了a[i]场胜利和b[i]场失利。而接下来还有m场比赛要进行。问联盟球队的最小总支出是多少。
输入格式:
第一行n,m
接下来n行每行4个整数a[i],b[i],Ci,Di
再接下来m行每行两个整数s,t表示第s支队伍和第t支队伍之间将有一场比赛,注意两只队间可能有多场比赛。
输出格式:
输出总支出的最小值。
输入样例#1:
3 3 1 0 2 1 1 1 10 1 0 1 3 3 1 2 2 3 3 1
输出样例#1:
43
对于20%的数据2<=n<=10,0<=m<=20
对于100%的数据2<=n<=5000,0<=m<=1000,0<=di<=ci<=10,0<=a[i],b[i]<=50.
这个的网络模型需要来表示下面m场比赛的胜负情况,我们考虑使用费用流。对比赛和队伍建点,建立源→比赛→参与比赛的两支队伍→汇的网络,其中源→比赛→队伍的边都是容量1费用0的边。
接下来考虑一下队伍→汇的边的费用问题。对于每一支队伍,我们假设他输掉了所有后面的x场比赛,也就是说,假如我们用w代表它赢的比赛,l代表它输的比赛,最开始的时候w=a_i, l=b_i+x,那么它的收益应该是C_iw^2+D_il^2。如果它赢了1场,则w加1,l减1,收益变为了C_i(w+1)^2+D_i(l-1)^2,我们来做一发减法,发现了\Delta = 2C_iw - 2D_il + C + D。我们知道,w越大的时候,l越小,\Delta的值就越大。因此这题就是一个费用递增模型,我们可以对每一个w建一条容量1费用2C_iw - 2D_il + C + D的边,表示每赢一场比赛对答案的贡献。此时这个网络模型就完整了,答案即是默认所有队伍输掉所有比赛的收益+最小费用最大流的费用。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, cap, cost, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 1];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int cap, int cost) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, cap, cost, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, 0, -cost, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int f[MAXN], dis[MAXN], pre[MAXN], pree[MAXN];
std::queue<int> que;
bool inque[MAXN];
inline bool spfa(int s, int t) {
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0; inque[s] = true; f[s] = INF; que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop(); inque[u] = false;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && dis[v] > dis[u] + gra[i].cost) {
pre[v] = u; pree[v] = i;
f[v] = std::min(f[u], gra[i].cap);
dis[v] = dis[u] + gra[i].cost;
if(!inque[v]) {
inque[v] = true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return f[t];
}
int flow, cost;
inline void mcmf(int s, int t) {
while(spfa(s, t)) {
for(int i = t; i != s; i = pre[i]) {
gra[pree[i]].cap -= f[t];
gra[pree[i] ^ 1].cap += f[t];
}
flow += f[t];
cost += f[t] * dis[t];
}
}
int n, m, a[MAXN], b[MAXN], c[MAXN], d[MAXN], mcnt[MAXN], u, v, sum, S, T;
// 1 ~ n team
// n+1 ~ n+m match
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = readint(); m = readint();
S = n + m + 1; T = S + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = readint(); b[i] = readint(); c[i] = readint(); d[i] = readint();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
u = readint(); v = readint();
mcnt[u]++; mcnt[v]++;
addedge(S, i + n, 1, 0);
addedge(i + n, u, 1, 0);
addedge(i + n, v, 1, 0);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int w = a[i], l = b[i] + mcnt[i];
sum += c[i] * w * w + d[i] * l * l;
for(int j = 1; j <= mcnt[i]; j++) {
addedge(i, T, 1, 2 * w * c[i] - 2 * l * d[i] + c[i] + d[i]);
w++; l--;
}
}
mcmf(S, T);
printf("%d", sum + cost);
return 0;
}
题目地址:洛谷:【P2046】[NOI2010]海拔 – 洛谷、BZOJ:Problem 2007. — [Noi2010]海拔
YT市是一个规划良好的城市,城市被东西向和南北向的主干道划分为n×n个区域。简单起见,可以将YT市看作 一个正方形,每一个区域也可看作一个正方形。从而,YT城市中包括(n+1)×(n+1)个交叉路口和2n×(n+1)条双向道路(简称道路),每条双向 道路连接主干道上两个相邻的交叉路口。下图为一张YT市的地图(n = 2),城市被划分为2×2个区域,包括3×3个交叉路口和12条双向道路。
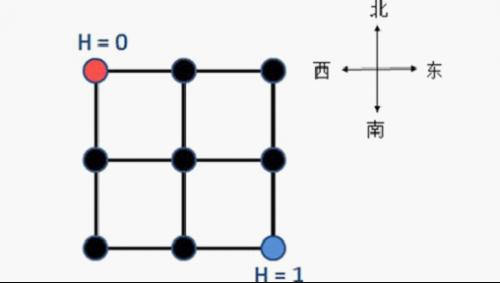
小Z作为该市的市长,他根据统计信息得到了每天上班高峰期间YT市每条道路两个方向的人流量,即在高峰期间沿 着该方向通过这条道路的人数。每一个交叉路口都有不同的海拔高度值,YT市市民认为爬坡是一件非常累的事情,每向上爬h的高度,就需要消耗h的体力。如果 是下坡的话,则不需要耗费体力。因此如果一段道路的终点海拔减去起点海拔的值为h(注意h可能是负数),那么一个人经过这段路所消耗的体力是max{0, h}(这里max{a, b}表示取a, b两个值中的较大值)。
小Z还测量得到这个城市西北角的交叉路口海拔为0,东南角的交叉路口海拔为1(如上图所示),但其它交叉路口的海拔高度都无法得知。小Z想知道在最理想的情况下(即你可以任意假设其他路口的海拔高度),每天上班高峰期间所有人爬坡消耗的总体力和的最小值。
输入格式:
第一行包含一个整数n,含义如上文所示。
接下来4n(n + 1)行,每行包含一个非负整数分别表示每一条道路每一个方向的人流量信息。输入顺序:n(n + 1)个数表示所有从西到东方向的人流量,然后n(n + 1)个数表示所有从北到南方向的人流量,n(n + 1)个数表示所有从东到西方向的人流量,最后是n(n + 1)个数表示所有从南到北方向的人流量。对于每一个方向,输入顺序按照起点由北向南,若南北方向相同时由西到东的顺序给出(参见样例输入)。
输出格式:
仅包含一个数,表示在最理想情况下每天上班高峰期间所有人爬坡所消耗的总体力和(即总体力和的最小值),结果四舍五入到整数。
输入样例#1:
1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
输出样例#1:
3
对于20%的数据:n ≤ 3;
对于50%的数据:n ≤ 15;
对于80%的数据:n ≤ 40;
对于100%的数据:1 ≤ n ≤ 500,0 ≤ 流量 ≤ 1,000,000且所有流量均为整数。
我们发现这些方格在最优解上的高度肯定非0即1,且有一条明显的分界线。因此我们只需要找出一些跨越分界线的边,计算它们的贡献即可。这实际上可以看成一个最小割。
既然我们把原问题转化成了最小割问题,就可以继续转化为对偶图上的最短路问题。由于是方格图,对偶图很好建立。
需要注意的是双向边问题,我们只需要在对偶图上也建立方向相反权值不同的有向边即可。例如我们将向下向右的边建为S→T方向,则向上向左的边要建为T→S方向,随后跑一遍最短路即可。通过验证,S、T的选择与边的方向选择的两种方案是等价的,因此可以任意选择S和T的位置。下面的代码中,上边界和右边界与T相连,下边界和左边界与S相连。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 1000005;
struct Edge {
int to, w, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 1];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int w) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, w, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
}
int dis[MAXN];
bool inque[MAXN];
struct Queue {
int l, r, q[MAXN];
inline void clear() {
l = r = 0;
}
Queue() {
clear();
}
inline int front() {
return q[l];
}
inline void push(int x) {
q[r++] = x;
if(r >= MAXN) r -= MAXN;
}
inline void pop() {
l++;
if(l >= MAXN) l -= MAXN;
}
inline bool empty() {
return l == r;
}
} que;
inline void spfa(int s) {
que.clear();
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0; inque[s] = true;
que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
register int u = que.front(); que.pop(); inque[u] = false;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
register int v = gra[i].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[u] + gra[i].w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + gra[i].w;
if(!inque[v]) {
inque[v] = true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
}
}
int n, t, S, T;
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = readint();
S = 0; T = n * n + 1;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
for(register int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
t = readint();
if(i == 1) {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j, T, t);
} else if(i == n + 1) {
addedge(S, (i - 2) * n + j, t);
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j, (i - 2) * n + j, t);
}
}
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(register int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) {
t = readint();
if(j == 1) {
addedge(S, (i - 1) * n + j, t);
} else if(j == n + 1) {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j - 1, T, t);
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j - 1, (i - 1) * n + j, t);
}
}
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
for(register int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
t = readint();
if(i == 1) {
addedge(T, (i - 1) * n + j, t);
} else if(i == n + 1) {
addedge((i - 2) * n + j, S, t);
} else {
addedge((i - 2) * n + j, (i - 1) * n + j, t);
}
}
}
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(register int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) {
t = readint();
if(j == 1) {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j, S, t);
} else if(j == n + 1) {
addedge(T, (i - 1) * n + j - 1, t);
} else {
addedge((i - 1) * n + j, (i - 1) * n + j - 1, t);
}
}
}
spfa(S);
printf("%d", dis[T]);
return 0;
}