Splay原理与实现

注:本文部分图片来自互联网,其相关权利归原作者所有,感谢原作者的分享。
概述
Splay(伸展树)是异于Treap的另一种平衡树,由Tarjan等发明。其滋磁的操作更为通用,因此被OIer广为使用。这里介绍Splay的原理与实现。
原理与实现
旋转
旋转操作与Treap相同,可以在Treap原理与实现 | KSkun’s Blog查看示例。这里将左右旋换为了一种自适应的写法。
下面是旋转的实现。
inline void rotate(int p) { // p is child
bool type = !isleft(p);
int fa = tr[p].fa, ffa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].ch[type] = tr[p].ch[!type];
tr[p].ch[!type] = fa;
tr[tr[fa].ch[type]].fa = fa;
if(ffa) tr[ffa].ch[!isleft(fa)] = p;
tr[p].fa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].fa = p;
calsiz(fa);
calsiz(p);
}
伸展
Splay(伸展)操作是Splay的核心功能,下面介绍Splay操作的原理。
我们需要讨论以下三种情况:
1. zig/zag式
zig/zag式,即为仅有两个节点,例如:
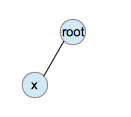
这种情况使用单旋,将儿子变为根。
2.zig-zag式
zig-zag式即儿子-父亲,父亲-祖先的左右儿子关系不相同,如下图。
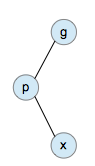
这种情况使用双旋,先转儿子,再转父亲。例如:
原树:
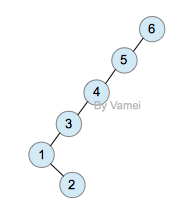
旋转后:
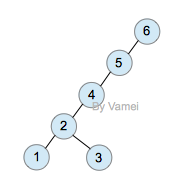
3.zig-zig式
zig-zag式即儿子-父亲,父亲-祖先的左右儿子关系相同,如下图。
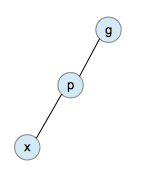
这种情况使用双旋,对儿子进行两次旋转。例如:
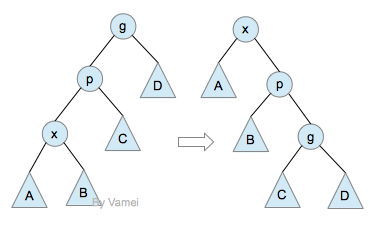
转完以后还是一个链啊?为什么会减小复杂度呢?
试想,既然原树不平衡,说明左侧子树较大,我们把一部分放在右侧,这样就会更平衡。
Splay操作的实现如下。
inline void splay(int p, int tar) {
for(int fa; (fa = tr[p].fa) != tar; rotate(p)) {
if(tr[tr[p].fa].fa != tar) {
rotate(isleft(fa) == isleft(p) ? fa : p);
}
}
if(!tar) rt = p;
}
splay(p, tar)的功能是将p旋转至tar的儿子。
插入/删除
与Treap的操作并无两样,就是需要在插入/删除后splay一下。详情见实现。
inline void insert(int val) {
if(!rt) {
rt = newnode();
tr[rt].val = val;
tr[rt].siz = tr[rt].cnt = 1;
return;
}
int p = rt, fa = 0;
for(;;) {
if(val == tr[p].val) {
tr[p].cnt++;
calsiz(p);
calsiz(fa);
splay(p);
return;
}
fa = p;
p = tr[p].ch[tr[p].val < val];
if(!p) {
p = newnode();
tr[p].val = val;
tr[p].siz = tr[p].cnt = 1;
tr[p].fa = fa;
tr[fa].ch[tr[fa].val < val] = p;
calsiz(fa);
splay(p);
return;
}
}
}
inline void delet(int val) {
queryrk(val);
if(tr[rt].cnt > 1) {
tr[rt].cnt--;
calsiz(rt);
return;
}
if(!tr[rt].ch[0]) {
delnode(rt);
rt = tr[rt].ch[1];
tr[rt].fa = 0;
return;
}
if(!tr[rt].ch[1]) {
delnode(rt);
rt = tr[rt].ch[0];
tr[rt].fa = 0;
return;
}
int ort = rt, lmx = querypre();
splay(lmx);
tr[rt].ch[1] = tr[ort].ch[1];
tr[tr[rt].ch[1]].fa = rt;
delnode(ort);
calsiz(rt);
}
其他
其他和Treap区别不大,可以看代码。
区间翻转
将整个数列按照顺序建一棵splay,权值代表数列的第几个数。区间翻转实质上可以通过交换左右儿子实现。而且通过打标记的形式可以做到lazy标记的效果。
在打标记之前,我们首先要把需要翻转的序列放进一个子树中。先splay l-1节点到根,再splay r+1节点到l-1节点儿子处。这样,根的右儿子的左儿子所在子树就是大于l-1小于r+1,即[l, r]区间。在这个子树的根打标记即可。但是要用到l-1和r+1,我们考虑加数列两端加-INF和INF两项,避免l-1和r+1越界。
Splay的中序遍历就是当前数列。
代码
常规操作
这份代码可以通过洛谷【P3369】【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) – 洛谷或BZOJProblem 3224. — Tyvj 1728 普通平衡树题目。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/2
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++;
}
inline int readint() {
register int res = 0, neg = 1;
char c = fgc();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
// variable
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
int n, op, x;
// splay
struct Node {
int ch[2], val, siz, cnt, fa;
} tr[MAXN];
int tot = 0, sta[MAXN], stop = 0, rt = 0, anst;
inline void calsiz(int p) {
tr[p].siz = tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[tr[p].ch[1]].siz + tr[p].cnt;
}
inline int newnode() {
int p;
if(stop > 0) {
p = sta[--stop];
} else {
p = ++tot;
}
memset(tr + p, 0, sizeof(Node));
return p;
}
inline void delnode(int a) {
sta[stop++] = a;
}
inline bool isleft(int p) {
return tr[tr[p].fa].ch[0] == p;
}
inline void rotate(int p) { // p is child
bool type = !isleft(p);
int fa = tr[p].fa, ffa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].ch[type] = tr[p].ch[!type];
tr[p].ch[!type] = fa;
tr[tr[fa].ch[type]].fa = fa;
if(ffa) tr[ffa].ch[!isleft(fa)] = p;
tr[p].fa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].fa = p;
calsiz(fa);
calsiz(p);
if(!tr[p].fa) rt = p;
}
inline void splay(int p) {
while(tr[p].fa) {
if(!tr[tr[p].fa].fa) {
rotate(p);
} else {
if(isleft(p) == isleft(tr[p].fa)) {
rotate(tr[p].fa);
rotate(p);
} else {
rotate(p);
rotate(p);
}
}
}
}
inline void insert(int val) {
if(!rt) {
rt = newnode();
tr[rt].val = val;
tr[rt].siz = tr[rt].cnt = 1;
return;
}
int p = rt, fa = 0;
for(;;) {
if(val == tr[p].val) {
tr[p].cnt++;
calsiz(p);
calsiz(fa);
splay(p);
return;
}
fa = p;
p = tr[p].ch[tr[p].val < val];
if(!p) {
p = newnode();
tr[p].val = val;
tr[p].siz = tr[p].cnt = 1;
tr[p].fa = fa;
tr[fa].ch[tr[fa].val < val] = p;
calsiz(fa);
splay(p);
return;
}
}
}
inline int queryrk(int val) {
int p = rt, ans = 0;
for(;;) {
if(val < tr[p].val) {
p = tr[p].ch[0];
} else {
ans += tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz;
if(val == tr[p].val) {
splay(p);
return ans + 1;
}
ans += tr[p].cnt;
p = tr[p].ch[1];
}
}
}
inline int queryn(int rk) {
int p = rt;
for(;;) {
if(tr[p].ch[0] && rk <= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz) {
p = tr[p].ch[0];
} else {
if(rk <= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[p].cnt) {
return tr[p].val;
}
rk -= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[p].cnt;
p = tr[p].ch[1];
}
}
}
inline int querypre() {
int p = tr[rt].ch[0];
while(tr[p].ch[1]) p = tr[p].ch[1];
return p;
}
inline int querynxt() {
int p = tr[rt].ch[1];
while(tr[p].ch[0]) p = tr[p].ch[0];
return p;
}
inline void delet(int val) {
queryrk(val);
if(tr[rt].cnt > 1) {
tr[rt].cnt--;
calsiz(rt);
return;
}
if(!tr[rt].ch[0]) {
delnode(rt);
rt = tr[rt].ch[1];
tr[rt].fa = 0;
return;
}
if(!tr[rt].ch[1]) {
delnode(rt);
rt = tr[rt].ch[0];
tr[rt].fa = 0;
return;
}
int ort = rt, lmx = querypre();
splay(lmx);
tr[rt].ch[1] = tr[ort].ch[1];
tr[tr[rt].ch[1]].fa = rt;
delnode(ort);
calsiz(rt);
}
int main() {
n = readint();
while(n--) {
op = readint();
x = readint();
switch(op) {
case 1:
insert(x);
break;
case 2:
delet(x);
break;
case 3:
printf("%d\n", queryrk(x));
break;
case 4:
printf("%d\n", queryn(x));
break;
case 5:
insert(x);
printf("%d\n", tr[querypre()].val);
delet(x);
break;
case 6:
insert(x);
printf("%d\n", tr[querynxt()].val);
delet(x);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
区间翻转
这份代码可以通过洛谷【P3391】【模板】文艺平衡树(Splay) – 洛谷或BZOJProblem 3223. — Tyvj 1729 文艺平衡树题目。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/2
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++;
}
inline int readint() {
register int res = 0, neg = 1;
char c = fgc();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
// variable
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
int n, m, ll, rr, data[MAXN];
// splay
struct Node {
int ch[2], val, siz, cnt, fa;
bool tag;
} tr[MAXN];
int tot = 0, sta[MAXN], stop = 0, rt = 0;
inline void calsiz(int p) {
tr[p].siz = tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[tr[p].ch[1]].siz + tr[p].cnt;
}
inline int newnode() {
int p;
if(stop > 0) {
p = sta[--stop];
} else {
p = ++tot;
}
memset(tr + p, 0, sizeof(Node));
return p;
}
inline void delnode(int a) {
sta[stop++] = a;
}
inline bool isleft(int p) {
return tr[tr[p].fa].ch[0] == p;
}
inline void rotate(int p) { // p is child
bool type = !isleft(p);
int fa = tr[p].fa, ffa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].ch[type] = tr[p].ch[!type];
tr[p].ch[!type] = fa;
tr[tr[fa].ch[type]].fa = fa;
if(ffa) tr[ffa].ch[!isleft(fa)] = p;
tr[p].fa = tr[fa].fa;
tr[fa].fa = p;
calsiz(fa);
calsiz(p);
}
inline void splay(int p, int tar) {
for(int fa; (fa = tr[p].fa) != tar; rotate(p)) {
if(tr[tr[p].fa].fa != tar) {
rotate(isleft(fa) == isleft(p) ? fa : p);
}
}
if(!tar) rt = p;
}
inline void pushdown(int p) {
if(tr[p].tag) {
if(tr[p].ch[0]) tr[tr[p].ch[0]].tag = !tr[tr[p].ch[0]].tag;
if(tr[p].ch[1]) tr[tr[p].ch[1]].tag = !tr[tr[p].ch[1]].tag;
std::swap(tr[p].ch[0], tr[p].ch[1]);
tr[p].tag = false;
}
}
inline int queryn(int rk) {
int p = rt;
for(;;) {
pushdown(p);
if(tr[p].ch[0] && rk <= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz) {
p = tr[p].ch[0];
} else {
if(rk <= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[p].cnt) {
return p;
}
rk -= tr[tr[p].ch[0]].siz + tr[p].cnt;
p = tr[p].ch[1];
}
}
}
inline int build(int fa, int l, int r) {
if(l > r) return 0;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1, p = newnode();
tr[p].val = data[mid];
tr[p].fa = fa;
tr[p].ch[0] = build(p, l, mid - 1);
tr[p].ch[1] = build(p, mid + 1, r);
tr[p].cnt = 1;
calsiz(p);
return p;
}
inline void reverse(int l, int r) {
int x = queryn(l), y = queryn(r + 2);
splay(x, 0);
splay(y, x);
tr[tr[tr[rt].ch[1]].ch[0]].tag = !tr[tr[tr[rt].ch[1]].ch[0]].tag;
}
inline void dfs(int p) {
pushdown(p);
if(tr[p].ch[0]) dfs(tr[p].ch[0]);
if(tr[p].val != -INF && tr[p].val != INF) {
printf("%d ", tr[p].val);
}
if(tr[p].ch[1]) dfs(tr[p].ch[1]);
}
int main() {
n = readint();
m = readint();
for(int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++) {
data[i] = i - 1;
}
data[1] = -INF;
data[n + 2] = INF;
rt = build(0, 1, n + 2);
while(m--) {
ll = readint();
rr = readint();
reverse(ll, rr);
}
dfs(rt);
return 0;
}
参考资料
- P3391 【模板】文艺平衡树(Splay) 题解
- bzoj3223: Tyvj 1729 文艺平衡树 平衡树上的区间翻转标记 – CSDN博客
- 史上第二详尽的平衡树(Splay)详解 – CSDN博客
- 纸上谈兵: 伸展树 (splay tree) – Vamei – 博客园
- Splay学习笔记 – CSDN博客
- splay复习小记 – CSDN博客
- Splay入门解析【保证让你看不懂(滑稽)】 – CSDN博客
文中图片也来源于参考资料。
