[APIO2012]派遣 题解
题目地址:洛谷:【P1552】[APIO2012]派遣 – 洛谷、BZOJ:P …
May all the beauty be blessed.
题目地址:POJ:1177 — Picture、vjudge:Picture – POJ 1177 – Virtual Judge、洛谷:【P1856】[USACO5.5]矩形周长Picture – 洛谷
A number of rectangular posters, photographs and other pictures of the same shape are pasted on a wall. Their sides are all vertical or horizontal. Each rectangle can be partially or totally covered by the others. The length of the boundary of the union of all rectangles is called the perimeter.
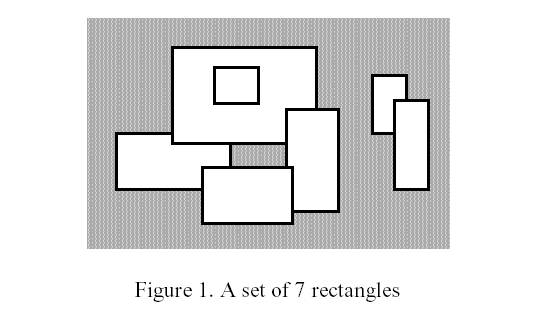
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
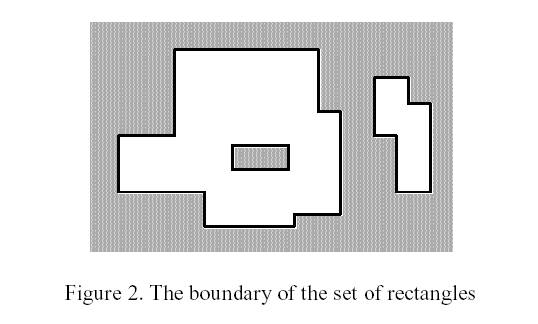
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.
给若干矩形,求矩形并的周长和(重叠的边只算一次,只计算外围周长)。
输入格式:
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains the number of rectangles pasted on the wall. In each of the subsequent lines, one can find the integer coordinates of the lower left vertex and the upper right vertex of each rectangle. The values of those coordinates are given as ordered pairs consisting of an x-coordinate followed by a y-coordinate.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
输出格式:
Your program is to write to standard output. The output must contain a single line with a non-negative integer which corresponds to the perimeter for the input rectangles.
输入样例#1:
7 -15 0 5 10 -5 8 20 25 15 -4 24 14 0 -6 16 4 2 15 10 22 30 10 36 20 34 0 40 16
输出样例#1:
228
本题是一个扫描线的经典应用,我们按x从小到大的顺序依次扫过矩形的每一条横边,统计这一条横边对答案的贡献(具体而言,就是加入这一段横边后对横向的覆盖的增量),动态维护现在已经覆盖的位置与连续的线段数,借由这些数据还可以顺便算出纵边对答案的贡献,每个连续的横向线段的两侧必然有2个对纵向周长产生贡献的线段。维护已覆盖的位置与连续的线段数可以用线段树实现。设计len表示已覆盖的长度,lin表示区间内连续的线段数。每次合并时len直接加,lin加完以后判断有没有直线跨两个儿子区间减掉重复算的就可以了。
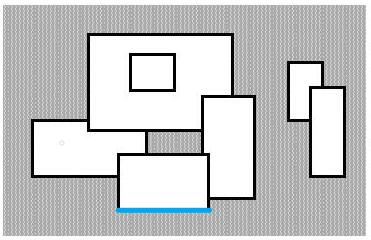
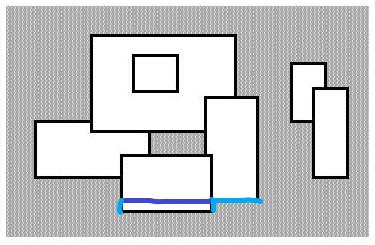
以题目附图为例,下面天蓝色表示扫到这一条线的时候对答案的贡献,深蓝色表示已经覆盖的位置。
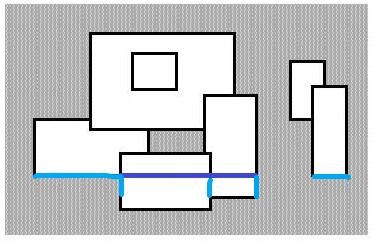
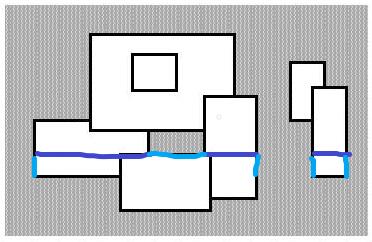
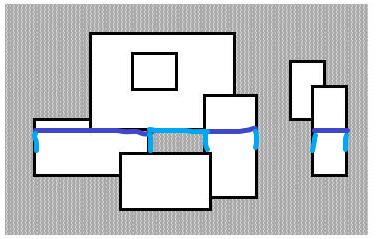
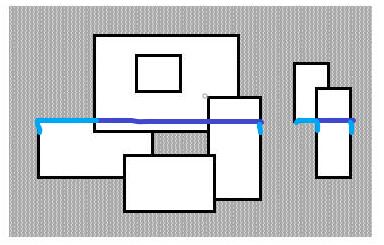
// Code by KSkun. 2018/2
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
struct Line {
int x, y1, y2, v;
} line[10005];
inline bool cmp(Line a, Line b) {
return a.x == b.x ? a.v > b.v : a.x < b.x;
}
int n, N, xa, ya, xb, yb, ans;
std::vector<int> vecy;
std::vector<int>::iterator yend;
// Segtree
#define lch o << 1
#define rch (o << 1) | 1
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
int val[40005], len[40005], lin[40005];
bool lft[40005], rgt[40005];
inline void callen(int o, int l, int r) {
if(val[o] > 0) {
len[o] = vecy[r - 1] - vecy[l - 1];
} else {
len[o] = len[lch] + len[rch];
}
}
inline void callin(int o, int l, int r) {
if(val[o] > 0) {
lft[o] = rgt[o] = true;
lin[o] = 1;
} else if(l == r) {
lft[o] = rgt[o] = false;
lin[o] = 0;
} else {
lft[o] = lft[lch];
rgt[o] = rgt[rch];
lin[o] = lin[lch] + lin[rch];
if(rgt[lch] && lft[rch]) lin[o]--;
}
}
inline void add(int o, int l, int r, int ll, int rr, int v) {
if(l == ll && r == rr) {
val[o] += v;
callen(o, l, r);
callin(o, l, r);
return;
}
if(rr <= mid) {
add(lch, l, mid, ll, rr, v);
} else if(ll >= mid) {
add(rch, mid, r, ll, rr, v);
} else {
add(lch, l, mid, ll, mid, v);
add(rch, mid, r, mid, rr, v);
}
callen(o, l, r);
callin(o, l, r);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &xa, &ya, &xb, &yb);
vecy.push_back(ya);
vecy.push_back(yb);
line[i].x = xa;
line[i].y1 = ya;
line[i].y2 = yb;
line[i].v = 1;
line[i + n].x = xb;
line[i + n].y1 = ya;
line[i + n].y2 = yb;
line[i + n].v = -1;
}
std::sort(vecy.begin(), vecy.end());
yend = std::unique(vecy.begin(), vecy.end());
N = yend - vecy.begin();
for(int i = 1; i <= n << 1; i++) {
line[i].y1 = std::lower_bound(vecy.begin(), yend, line[i].y1) - vecy.begin() + 1;
line[i].y2 = std::lower_bound(vecy.begin(), yend, line[i].y2) - vecy.begin() + 1;
}
std::sort(line + 1, line + (n << 1) + 1, cmp);
line[0].x = -1e9;
int lastlen = 0, lastlin = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n << 1; i++) {
add(1, 1, N, line[i].y1, line[i].y2, line[i].v);
if(i > 1) ans += 2 * lastlin * (line[i].x - line[i - 1].x);
ans += std::abs(len[1] - lastlen);
lastlen = len[1];
lastlin = lin[1];
}
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
题目地址:Codeforces:Problem – 714C – Codeforces、vjudge:Sonya and Queries – CodeForces 714C – Virtual Judge
Today Sonya learned about long integers and invited all her friends to share the fun. Sonya has an initially empty multiset with integers. Friends give her t queries, each of one of the following type:
+ ai — add non-negative integer ai to the multiset. Note, that she has a multiset, thus there may be many occurrences of the same integer.- ai — delete a single occurrence of non-negative integer ai from the multiset. It’s guaranteed, that there is at least one ai in the multiset.? s — count the number of integers in the multiset (with repetitions) that match some pattern s consisting of 0 and 1. In the pattern, 0 stands for the even digits, while 1 stands for the odd. Integer x matches the pattern s, if the parity of the i-th from the right digit in decimal notation matches the i-th from the right digit of the pattern. If the pattern is shorter than this integer, it’s supplemented with 0-s from the left. Similarly, if the integer is shorter than the pattern its decimal notation is supplemented with the 0-s from the left.For example, if the pattern is s = 010, than integers 92, 2212, 50 and 414 match the pattern, while integers 3, 110, 25 and 1030 do not.
用0代替十进制数中的偶数数码,1代替奇数数码,有三种操作:插入,插入一个十进制数;删除,删除一个已经插入的十进制数;查询,查询符合给定01串的数的个数,符合定义为从右往左与给定串的01数码相同,如果长度不一在左边补0。
输入格式:
The first line of the input contains an integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 100 000) — the number of operation Sonya has to perform.
Next t lines provide the descriptions of the queries in order they appear in the input file. The i-th row starts with a character ci — the type of the corresponding operation. If ci is equal to + or - then it’s followed by a space and an integer ai (0 ≤ ai < 10^{18}) given without leading zeroes (unless it’s 0). If ci equals ‘?’ then it’s followed by a space and a sequence of zeroes and onse, giving the pattern of length no more than 18.
It’s guaranteed that there will be at least one query of type ?.
It’s guaranteed that any time some integer is removed from the multiset, there will be at least one occurrence of this integer in it.
输出格式:
For each query of the third type print the number of integers matching the given pattern. Each integer is counted as many times, as it appears in the multiset at this moment of time.
样例输入1:
12 + 1 + 241 ? 1 + 361 - 241 ? 0101 + 101 ? 101 - 101 ? 101 + 4000 ? 0
样例输出1:
2 1 2 1 1
样例输入2:
4 + 200 + 200 - 200 ? 0
样例输出2:
1
样例1说明:
Consider the integers matching the patterns from the queries of the third type. Queries are numbered in the order they appear in the input.
这个题乍看一下很有意思。分析一下三种操作,我们发现如果长度不一且长的那个多出来的部分里有1就不能加入答案,于是我们思考能不能把左边的前导0全删去,再反着插入Trie树,这样构建的01Trie直接查询就可以了。对于输入的每个字符串都如此操作,插入删除以及查找都是常规操作。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/2
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
const int tab[10] = {0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1};
int trie[1800005][2], wrd[1800005], siz = 1;
inline bool isop(char c) {
return c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '?';
}
inline void insert(char* str, int l, int r) {
int t = 1;
for(int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
if(!trie[t][str[i] - '0']) {
t = trie[t][str[i] - '0'] = ++siz;
} else {
t = trie[t][str[i] - '0'];
}
}
wrd[t]++;
}
inline int search(char* str, int l, int r) {
int t = 1;
for(int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
if(!trie[t][str[i] - '0']) {
return 0;
} else {
t = trie[t][str[i] - '0'];
}
}
return wrd[t];
}
inline void delet(char* str, int l, int r) {
int t = 1;
for(int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
if(!trie[t][str[i] - '0']) {
return;
} else {
t = trie[t][str[i] - '0'];
}
}
wrd[t]--;
}
inline int proc(char* str) {
int len = strlen(str), res = len - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
str[i] = tab[str[i] - '0'] + '0';
if(str[i] == '1' && res == len - 1) res = i;
}
return res;
}
int t;
char op, str[20];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &t);
for(int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
while(!isop(op = getchar()));
scanf("%s", str);
if(op == '+') {
insert(str, proc(str), strlen(str) - 1);
} else if(op == '-') {
delet(str, proc(str), strlen(str) - 1);
} else {
printf("%d\n", search(str, proc(str), strlen(str) - 1));
}
}
return 0;
}