[GCJ2014R2]Don’t Break The Nile 题解
题目地址:Google Code:Dashboard – Round 2 20 …
May all the beauty be blessed.
题目地址:洛谷:【P4001】[BJOI2006]狼抓兔子 – 洛谷、BZOJ:Problem 1001. — [BeiJing2006]狼抓兔子
现在小朋友们最喜欢的”喜羊羊与灰太狼”,话说灰太狼抓羊不到,但抓兔子还是比较在行的,而且现在的兔子还比较笨,它们只有两个窝,现在你做为狼王,面对下面这样一个网格的地形:
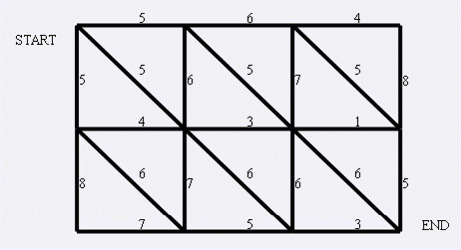
左上角点为(1,1),右下角点为(N,M)(上图中N=3,M=4).有以下三种类型的道路
1:(x,y)<==>(x+1,y)
2:(x,y)<==>(x,y+1)
3:(x,y)<==>(x+1,y+1)
道路上的权值表示这条路上最多能够通过的兔子数,道路是无向的. 左上角和右下角为兔子的两个窝,开始时所有的兔子都聚集在左上角(1,1)的窝里,现在它们要跑到右下角(N,M)的窝中去,狼王开始伏击这些兔子.当然为了保险起见,如果一条道路上最多通过的兔子数为K,狼王需要安排同样数量的K只狼,才能完全封锁这条道路,你需要帮助狼王安排一个伏击方案,使得在将兔子一网打尽的前提下,参与的狼的数量要最小。因为狼还要去找喜羊羊麻烦。
输入格式:
第一行为N,M.表示网格的大小,N,M均小于等于1000.
接下来分三部分
第一部分共N行,每行M-1个数,表示横向道路的权值.
第二部分共N-1行,每行M个数,表示纵向道路的权值.
第三部分共N-1行,每行M-1个数,表示斜向道路的权值.
输出格式:
输出一个整数,表示参与伏击的狼的最小数量.
输入样例#1:
3 4 5 6 4 4 3 1 7 5 3 5 6 7 8 8 7 6 5 5 5 5 6 6 6
输出样例#1:
14
我们可以直接按照图示建立网络,求最小割。Dinic跑是很快的。
这有个讲解对偶图的ppt:点击下载
然后我们可以利用对偶图的性质,建立对偶图,求S到T的最短路,即为最小割。这样来做点数边数能够变小,避免了空间爆炸的情况。
下面的代码中,建图的规律是第一行右上三角形的编号为1~m-1,左下三角形的编号为m~2m-2,底下以此类推。需要判断越界的面属于S还是T。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 2000005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, cap, nxt;
} gra[MAXN * 5];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int cap) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, cap, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, cap, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int level[MAXN];
inline bool bfs(int s, int t) {
memset(level, -1, sizeof(level));
std::queue<int> que;
level[s] = 0; que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(level[v] == -1 && gra[i].cap > 0) {
level[v] = level[u] + 1;
if(v == t) return true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
return level[t] != -1;
}
int cur[MAXN];
inline int dfs(int u, int t, int left) {
if(u == t || left <= 0) return left;
int flow = 0;
for(int &i = cur[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && level[v] == level[u] + 1) {
int d = dfs(v, t, std::min(left, gra[i].cap));
if(d > 0) {
flow += d; left -= d;
gra[i].cap -= d; gra[i ^ 1].cap += d;
if(left <= 0) break;
}
}
}
return flow;
}
inline int dinic(int s, int t) {
int flow = 0;
while(bfs(s, t)) {
memcpy(cur, head, sizeof(head));
int f;
while(f = dfs(s, t, INF)) {
flow += f;
}
}
return flow;
}
int n, m, t;
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = readint(); m = readint();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
t = readint();
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, (i - 1) * m + j + 1, t);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
t = readint();
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, i * m + j, t);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
t = readint();
addedge((i - 1) * m + j, i * m + j + 1, t);
}
}
printf("%d", dinic(1, n * m));
return 0;
}
参考资料:【BJOI2006】狼抓兔子 – flow丶 – 博客园
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 2000005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, w, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 2];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int w) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, w, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, w, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int dis[MAXN];
bool inque[MAXN];
inline void spfa(int s) {
std::queue<int> que;
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0; inque[s] = true;
que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop(); inque[u] = false;
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[u] + gra[i].w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + gra[i].w;
if(!inque[v]) {
inque[v] = true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
}
}
int n, m, t, S, T;
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = readint(); m = readint();
S = 0; T = (n - 1) * (m - 1) * 2 + 1;
int u = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
t = readint();
int v = u - (m - 1), u1 = u, v1 = v;
if(v <= S) v1 = S;
if(u >= T) u1 = T;
addedge(u1, v1, t);
u++;
}
u += m - 1;
}
u = m;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
t = readint();
int v = u - m, u1 = u, v1 = v;
if(v <= 2 * (i - 1) * (m - 1)) v1 = T;
if(u > 2 * i * (m - 1)) u1 = S;
addedge(u1, v1, t);
u++;
}
u += m - 2;
}
u = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
t = readint();
addedge(u, u + m - 1, t);
u++;
}
u += m - 1;
}
spfa(S);
printf("%d", dis[T]);
return 0;
}
题目地址:洛谷:【P4174】[NOI2006]最大获利 – 洛谷、BZOJ:Problem 1497. — [NOI2006]最大获利
新的技术正冲击着手机通讯市场,对于各大运营商来说,这既是机遇,更是挑战。THU 集团旗下的 CS&T 通讯公司在新一代通讯技术血战的前夜,需要做太多的准备工作,仅就站址选择一项,就需要完成前期市场研究、站址勘测、最优化等项目。
在前期市场调查和站址勘测之后,公司得到了一共 N 个可以作为通讯信号中转站的地址,而由于这些地址的地理位置差异,在不同的地方建造通讯中转站需要投入的成本也是不一样的,所幸在前期调查之后这些都是已知数据:建立第 i个通讯中转站需要的成本为 Pi(1≤i≤N)。
另外公司调查得出了所有期望中的用户群,一共 M 个。关于第 i 个用户群的信息概括为 Ai, Bi和 Ci:这些用户会使用中转站 Ai 和中转站 Bi 进行通讯,公司可以获益 Ci。(1≤i≤M, 1≤Ai,Bi≤N)
THU 集团的 CS&T 公司可以有选择的建立一些中转站(投入成本),为一些用户提供服务并获得收益(获益之和)。那么如何选择最终建立的中转站才能让公司的净获利最大呢?(净获利 = 获益之和 – 投入成本之和)
输入格式:
输入文件中第一行有两个正整数 N 和 M 。
第二行中有 N 个整数描述每一个通讯中转站的建立成本,依次为 P1,P2,…,PN。
以下 M 行,第(i + 2)行的三个数 Ai,Bi和 Ci描述第 i 个用户群的信息。
所有变量的含义可以参见题目描述。
输出格式:
你的程序只要向输出文件输出一个整数,表示公司可以得到的最大净获利。
输入样例#1:
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 2 3 4 1 3 3 1 4 2 4 5 3
输出样例#1:
4
样例:选择建立 1、2、3 号中转站,则需要投入成本 6,获利为 10,因此得到最大收益 4。
100%的数据中:N≤5 000,M≤50 000,0≤ Ci ≤100,0≤ Pi ≤100。
这类问题有一个统一的模型,叫最大权闭合子图。
我们把中转站向汇连边,容量为建设成本。把客户向源连边,容量为获利。再把客户和用到的中转站之间连边,容量无限。求一次最小割,然后用所有获利减去这个最小割的权值和即为答案。
最小割肯定不会去割中间容量无限的边,因此割的是与源汇相连的边。割掉客户与源相连的边的含义是不要这个客户了,割掉中转站与汇相连的边的含义是不建这个中转站了。因此最小割的含义是发展客户净利润为负的收益加上建设中转站的总成本,也就是损失的收益+建设的开支,直接用总收益减去它就是答案。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, cap, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 3];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int cap) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, cap, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, 0, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int level[MAXN];
inline bool bfs(int s, int t) {
memset(level, -1, sizeof(level));
std::queue<int> que;
level[s] = 0; que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(level[v] == -1 && gra[i].cap > 0) {
level[v] = level[u] + 1;
if(v == t) return true;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
return level[t] != -1;
}
int cur[MAXN];
inline int dfs(int u, int t, int left) {
if(u == t || left <= 0) return left;
int flow = 0;
for(int &i = cur[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && level[v] == level[u] + 1) {
int d = dfs(v, t, std::min(left, gra[i].cap));
if(d > 0) {
left -= d; flow += d;
gra[i].cap -= d; gra[i ^ 1].cap += d;
if(left <= 0) {
//level[u] = -1; 不注释掉会TLE
return flow;
}
}
}
}
return flow;
}
inline int dinic(int s, int t) {
int flow = 0;
while(bfs(s, t)) {
memcpy(cur, head, sizeof(head));
int f;
while(f = dfs(s, t, INF)) {
flow += f;
}
}
return flow;
}
int n, m, pi, ai, bi, ci, S, T, ans;
// 1 ~ n device
// n+1 ~ n+m custom
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
n = readint(); m = readint();
S = n + m + 1; T = S + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pi = readint();
addedge(i, T, pi);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
ai = readint(); bi = readint(); ci = readint();
ans += ci;
addedge(S, n + i, ci);
addedge(n + i, ai, INF);
addedge(n + i, bi, INF);
}
ans -= dinic(S, T);
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
题目地址:POJ:1149 — PIGS、OpenJudge百练:OpenJudge – 1149:PIGS
Mirko works on a pig farm that consists of M locked pig-houses and Mirko can’t unlock any pighouse because he doesn’t have the keys. Customers come to the farm one after another. Each of them has keys to some pig-houses and wants to buy a certain number of pigs.
All data concerning customers planning to visit the farm on that particular day are available to Mirko early in the morning so that he can make a sales-plan in order to maximize the number of pigs sold.
More precisely, the procedure is as following: the customer arrives, opens all pig-houses to which he has the key, Mirko sells a certain number of pigs from all the unlocked pig-houses to him, and, if Mirko wants, he can redistribute the remaining pigs across the unlocked pig-houses.
An unlimited number of pigs can be placed in every pig-house.
Write a program that will find the maximum number of pigs that he can sell on that day.
有m个猪圈,每个猪圈里初始时有若干头猪。一开始所有猪圈都是关闭的。依次来了n个顾客,每个顾客分别会打开指定的几个猪圈,从中买若干头猪。
每个顾客分别都有他能够买的数量的上限。
每个顾客走后,他打开的那些猪圈中的猪,都可以被任意地调换到其它开着的猪圈里,然后所有猪圈重新关上。
问最多总共能卖出多少头猪。
输入格式:
The first line of input contains two integers M and N, 1 <= M <= 1000, 1 <= N <= 100, number of pighouses and number of customers. Pig houses are numbered from 1 to M and customers are numbered from 1 to N.
The next line contains M integeres, for each pig-house initial number of pigs. The number of pigs in each pig-house is greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 1000.
The next N lines contains records about the customers in the following form ( record about the i-th customer is written in the (i+2)-th line):
A K1 K2 … KA B It means that this customer has key to the pig-houses marked with the numbers K1, K2, …, KA (sorted nondecreasingly ) and that he wants to buy B pigs. Numbers A and B can be equal to 0.
输出格式:
The first and only line of the output should contain the number of sold pigs.
输入样例#1:
3 3 3 1 10 2 1 2 2 2 1 3 3 1 2 6
输出样例#1:
7
我们有一个想法就是根据时间拆点,把每个猪圈拆成n个点,分别代表n个顾客来的时候的状态。最开始的点与源连边,控制这个猪圈内的猪数量。每次顾客要买的猪圈与顾客连边,表示买猪。上一层与下一层猪圈连边,表示继承关系。上一层顾客打开的猪圈两两连边,表示猪的调换。但是我们容易发现这个图的点数O(nm)边数更是O(m^3),会TLE的。
我们换一种想法,如果有一个顾客想买猪,肯定是从他要买的猪圈的上一个顾客买剩下的猪里买。那么对于每个猪圈,它的猪是从上一个顾客向下一个顾客卖的,因此我们可以对于每个猪圈顾客依次连边。至于猪在不同猪圈的调换,如果下一个顾客的猪圈内部发生调换,容易发现这些猪圈都对应同一个顾客,而顾客点流过的流量代表的是总和,因此猪圈的调换也就不用再管了。这个图的点数O(n)边数O(nm),瞬间变小了不少。
// Code by KSkun, 2018/4
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
typedef long long LL;
inline char fgc() {
static char buf[100000], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
return p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF
: *p1++;
}
inline LL readint() {
register LL res = 0, neg = 1;
register char c = fgc();
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {
if(c == '-') neg = -1;
c = fgc();
}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
res = res * 10 + c - '0';
c = fgc();
}
return res * neg;
}
const int MAXN = 100005, INF = 1e9;
struct Edge {
int to, cap, nxt;
} gra[MAXN << 1];
int head[MAXN], tot;
inline void addedge(int u, int v, int cap) {
gra[tot] = Edge {v, cap, head[u]}; head[u] = tot++;
gra[tot] = Edge {u, 0, head[v]}; head[v] = tot++;
}
int level[MAXN];
std::queue<int> que;
inline bool bfs(int s, int t) {
memset(level, -1, sizeof(level));
level[s] = 0; que.push(s);
while(!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && level[v] == -1) {
level[v] = level[u] + 1;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
return level[t] != -1;
}
int cur[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
inline int dfs(int u, int t, int left) {
if(u == t || !left)
return left;
int flow = 0; vis[u] = true;
for(int &i = cur[u]; ~i; i = gra[i].nxt) {
int v = gra[i].to;
if(gra[i].cap > 0 && !vis[v] && level[v] == level[u] + 1) {
int d = dfs(v, t, std::min(left, gra[i].cap));
if(d > 0) {
left -= d; flow += d;
gra[i].cap -= d; gra[i ^ 1].cap += d;
if(!left) {
level[u] = -1;
return flow;
}
}
}
}
return flow;
}
inline int dinic(int s, int t) {
int flow = 0;
while(bfs(s, t)) {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memcpy(cur, head, sizeof(head));
int f;
while(f = dfs(s, t, INF)) {
flow += f;
}
}
return flow;
}
int m, n, pnum[MAXN], a, t, S, T;
std::vector<int> list[MAXN];
// 1 ~ n customers
int main() {
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
m = readint(); n = readint();
S = n + 1; T = S + 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
pnum[i] = readint();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a = readint();
for(int j = 1; j <= a; j++) {
t = readint();
list[t].push_back(i);
}
addedge(i, T, readint());
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if(!list[i].empty()) {
addedge(S, list[i][0], pnum[i]);
for(int j = 1; j < list[i].size(); j++) {
addedge(list[i][j - 1], list[i][j], INF);
}
}
}
printf("%d", dinic(S, T));
return 0;
}